Over the years, the textile Industry waste is extensively contributing to climate change in almost all the countries. There is no doubt that addiction towards buying fashion clothes is the most popular trend now a days. Shopping clothes has always been a fun and every time we go, we enjoy shopping and try new styles of shoes, jeans, tops, jackets, and more to become a part of those trends. With growing awareness about sustainability, recycling and reusing textile leftover has become a key strategy for reducing waste and conserving resources in the textile and fashion industries.
This is because of actually we are buying more clothes than ever before. Most clothes last many years but fast emerging fashions trends and discount sales have artificially shortened our changing tastes.
But it is a matter of fact that none of us even think about where all that clothes go after some time after we use them. The fashion industry is a leading industrial polluter worldwide, responsible for about 10% of global carbon emissions which is more than international flights and maritime shipping combined.
Regulating Textile Recycling Practices in United States
The recent bill passed in California will lead to putting a burden on clothing producers to implement a system for recycling the fabrics that they sell. This first-in-the-nation bill, known as the Responsible Textile Recovery Act was endorsed by 150 environmental organizations in US and would require the Producers Responsibility Organization (PRO) to submit a complete plan for the collection, transportation, repair, sorting, and recycling, and the safe and proper management of recyclable apparel and textile articles in the state.
Where Does the Textile Waste Come From
There is an estimated 95% of the materials in textile clothing including fabrics, yarns, fibers, zippers and buttons which are recyclable but approximately 85% of all textiles is either burnt or piled up in landfills emitting methane gas and leach chemicals and dyes into our soil and groundwater.
Rest of that gets reused by thrift stores, charities and clothing collectors or recycled through waste management techniques. According to reports an average American now generates 82 pounds of textile waste each year. This adds up to more than 11 million tons of textile waste from the US alone.
Apart from fabrics, leather production is increasingly linked to a variety of environmental and human health hazards. Leather tanning process is one of the most toxic in all of the fashion sector.
On one side the workers are exposed to harmful chemicals and on other side the untreated waste generated from this industry pollutes natural water resources leading to increased disease for surrounding areas. Studies have found that leather tannery workers are at a far greater risk of cancer also.

Useful Ways of Disposal of Used Garments
Material to material recycling for example by turning woolen clothes to carpets. There are many other ideas like;- Transform T-Shirts into cleaning rags, Bags, headbands, ribbons, quilts and pillows etc. There are numerous DIY ideas.
- Turn Socks into Heating Pads and jeans into shorts.
- Convert Sweaters Into colorful and comfortable Scarves
- Re-dye the faint colored garments to give them a new look
- Re-fashion it to new fashion by adding charms, pockets, pictures and gemstones or cutting any part to give it a new look. If you are creative there are endless DIY ideas here.
- Selling usable garments to thrift stores for reuse by lower income groups.
- Charity stores
- Export the garments which are not torn or stained to certain South American, Asian and African countries
- Stuffing Car seats

Use of recycled Garments – an Emerging Trend
In contrast to the sustainability of the textile garments, their sustainability and recycling, there are emerging trends of using recycled fabrics prepared from post-consumer waste. So, by choosing eco-friendly fabrics alone, we are a huge step ahead towards a more sustainable clothing.
Conventional fabrics used in fashion and home articles like cotton, viscose fabric and leather are prepared through many processes like plasticizing, bleaching, softening, and dyeing.
These manufacturing processes include usage of hundreds of type of chemical agents such as acids, alkalis, salts, oxidants, and reducers extensively damaging the ground water and eco system. The increasing demands of recycled textile products would help reduce the proportion of conventional textile products.
Recycled fabrics are normally prepared from materials obtained by recycling of post-consumer waste. There are 3 most common ways to process these fabric wastes.
- Mechanical shredding or pulling of fabric to transform them into fibers of shorter length for use in thermal insulation or carpet making and even in recycled fabrics.
- Chemical recycling for fabrics of one type of fiber, for example polyester and nylon is also workable. Although it needs multiple processes and additional chemicals making the fabric costly.
- Bio-recycling of fabrics to recover polyester (PET) fibers and yarn for use in further making of apparel and certain household hygiene products. However, there are few drawbacks as the recycled polyester still sheds microplastics and there are concerns over their toxicity. These issues can be resolved by checking for certifications that guarantee non-toxic materials have been used by the manufacturer.
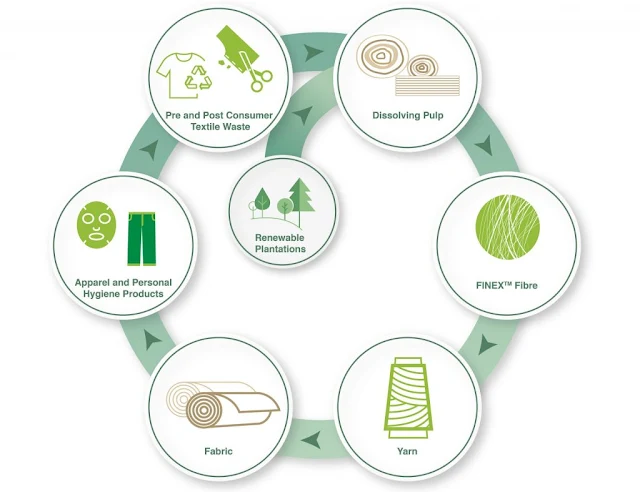
Common Types of Recycled Fabrics
- Recycled cotton fabrics are produced using either post-industrial or post-consumer waste, landfills, industry fabric scrap or other recycled cotton garments. However, sometimes it becomes difficult to know whether recycled cotton is 100% pure because a garment can be categorized as recycled cotton even if it bears 4% or less synthetic fibers.
- Organic linen is derived from the flax plant, whose growth requires little to no fertilizer, pesticide, and irrigation inputs. However, organic linen mostly grows in specific climates (Europe, mainly), which makes it a bit more of a luxury commodity.
- Recycled woolen fabrics are created from the recycling of used wool products such as old sweaters, scarves, or hats. The recycling process begins with collecting and sorting these used wool items, which are then cut into small pieces and recycled into new wool fibers to produce new woolen fabrics.
Recycling wool reduces the need for producing new wool, thereby conserving natural resources, water, and energy consumption during wool production. However, old wool items may contain a mix of various other fibers during the recycling process, which can reduce the reusability of the recycled wool fabric.

Conclusion
While the fashion sector is booming, there is an increased attention towards negative environmental impacts that the industry is responsible for. The fashion industry is the second-biggest consumer of water at the moment. The relatively fast changing trends, attitudes, advertisements and artificially decreased lifecycle of garments has led to excessive consumption of garments worldwide.
Here, the only way is to educate the people to change their behaviors in buying garments so rapidly. This will surely contribute towards sustainability of the environment and of course the textile products as well.
Additionally, recycled fabrics helps reduce waste, conserve natural resources, and minimize greenhouse gas emissions and pollutants released into the environment. By recycling and reusing used fabrics, we alleviate the pressure on natural resources and preserve the environment for future generations.
The responsibility also lies with the consumers and fashion industry to support the trends prioritizing the purchase and use of products made from recycled fabrics.


Comments
Post a Comment